Authored by Dr. Leland Jaffe, Associate Dean and Professor; Published on February 12th, 2024
Far too often in school (especially medical education), students hear negative feedback about what they’re doing wrong. I’m here to say that the use of positive feedback is a powerful tool that is very much underutilized. Feedback serves as a cornerstone in the educational journey, shaping not only academic performance but also fostering a supportive learning environment conducive to student success. In this blog post, we delve into the significance of positive feedback in higher education and its profound impact on students, educators, and the learning community as a whole. We’ll also outline the different types of positive reinforcement and how they can be implemented into your teaching style.
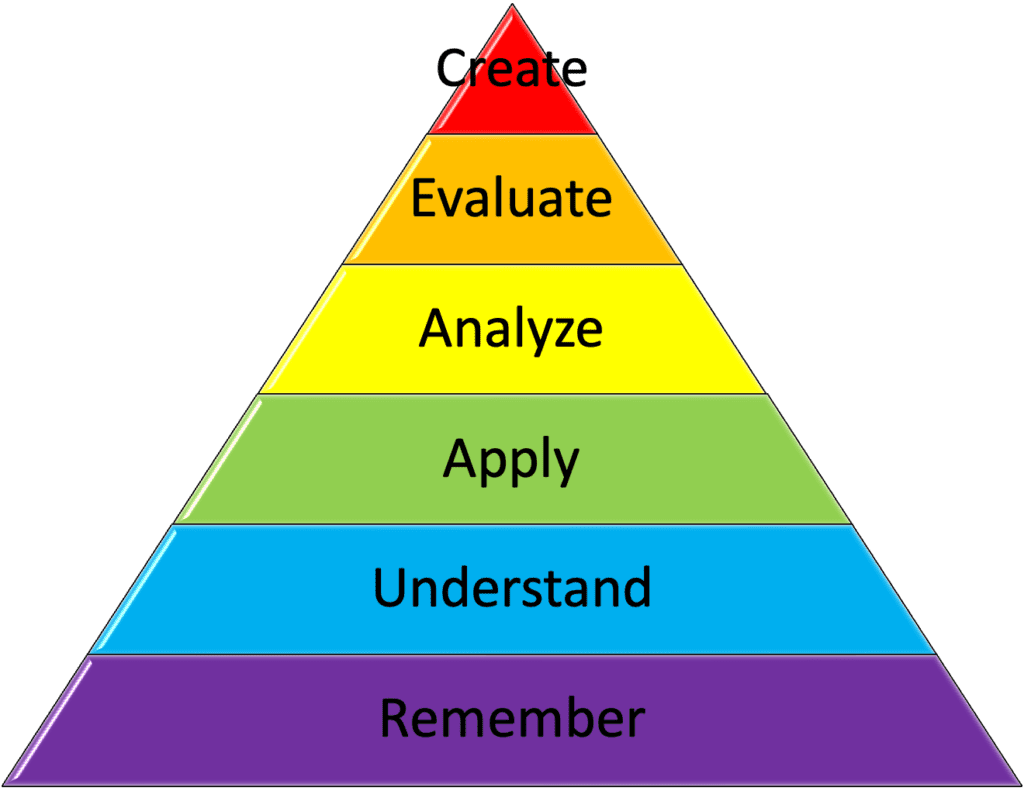
Fostering Growth Mindset
Positive feedback plays a pivotal role in nurturing a growth mindset among students. When students receive constructive and encouraging feedback on doing a good job, they are more inclined to view challenges as opportunities for growth rather than insurmountable obstacles. This mindset shift empowers students to embrace learning with resilience and perseverance, propelling them toward academic excellence and long-term personal development.
Examples of how creating a positive learning environment can help to facilitate a growth mindset
- Emphasizing Effort: When educators praise students for their hard work, resilience, and dedication, it reinforces the idea that progress comes from effort rather than innate ability. For example, saying, “I admire how you tackled that challenging concept by persistently seeking clarification and practicing until you understood it,” encourages students to view challenges as opportunities for growth rather than obstacles.
- Highlighting Progress: Recognizing and celebrating students’ progress and improvement is an example of positive reinforcement that strengthens the belief that abilities can be developed over time. For instance, acknowledging, “I’ve noticed how your problem-solving skills have improved since the beginning of the semester. Your commitment to learning and applying new strategies is paying off,” encourages students to focus on their journey of development rather than comparing themselves to others.
- Framing Mistakes as Learning Opportunities: Providing constructive feedback on mistakes and errors helps students understand that setbacks are a natural part of the learning process. For example, saying, “Your analysis of the case study was insightful, and your diagnosis was mostly accurate. Let’s explore areas where you can further refine your diagnostic reasoning to enhance your clinical decision-making skills,” encourages students to view mistakes as opportunities for reflection, learning, and growth.
- Encouraging Risk-Taking: Creating a supportive environment where students feel safe to take risks and try new approaches without fear of failure fosters a growth mindset. For instance, saying, “I appreciate your willingness to explore alternative treatment options for the patient, even though they may not always yield the desired outcome. It’s through experimentation and innovation that we learn and improve,” encourages students to step out of their comfort zones and embrace challenges as opportunities for learning and innovation.
- Modeling a Growth Mindset: Educators who demonstrate a growth mindset in their teaching and interactions serve as powerful role models for students. By sharing their struggles, failures, and successes, and emphasizing the importance of continuous learning and improvement, educators inspire students to adopt a similar mindset. For example, saying, “I encountered difficulties when I first learned this concept, but with persistence and practice, I was able to master it. Remember, learning is a journey, not a destination,” encourages students to approach their learning with optimism, resilience, and a belief in their potential for growth.
Enhancing Motivation and Engagement Through Positive Reinforcement


Effective feedback acts as a motivator, inspiring students to stay engaged and committed to their learning journey. By acknowledging students’ strengths and accomplishments, educators reinforce their intrinsic motivation, fueling a sense of purpose and pride in their academic pursuits. Moreover, positive feedback fosters a sense of belonging and encourages active participation in classroom discussions and collaborative activities, enhancing the overall learning experience.
Positive reinforcement in higher education can enhance motivation in students in several ways:
- Validation of Efforts: When students receive positive feedback, it validates their hard work and dedication and can have a significant positive impact on their classroom and clinical performance. Receiving positive comments about their performance can boost their confidence and motivation to continue striving for excellence.
- Increased Self-Efficacy: Receiving verbal praise reinforces students’ belief in their abilities to succeed academically and professionally. As they receive affirmation of their competencies, they develop a greater sense of self-efficacy, leading to increased motivation to tackle challenges and pursue their goals.
- Sense of Progress: Constructive feedback highlights areas where students excel, as well as areas for improvement. When students see specific evidence of their progress, it fuels their motivation to keep pushing forward and striving for further growth and development.
- Enhanced Engagement: Positive feedback fosters a supportive learning environment where students feel valued and engaged. This creates a positive cycle where motivated students actively participate in class, seek out learning opportunities, and collaborate with peers, leading to further positive outcomes and reinforcement.
- Boost in Confidence: Receiving positive feedback can boost students’ confidence in their clinical skills, diagnostic abilities, and patient care. This confidence not only motivates students to continue excelling in their studies but is a great way to help prepare them for their future roles as healthcare professionals.
- Promotion of Intrinsic Motivation: Positive feedback that focuses on students’ strengths and accomplishments can help cultivate intrinsic motivation—the drive to engage in activities for their inherent enjoyment and satisfaction. As students experience the intrinsic rewards of learning and mastering medical knowledge and skills, they become more motivated to pursue their educational and career goals with enthusiasm and dedication.
- Sense of Belonging: Positive feedback fosters a sense of belonging and connection within the medical school community. When students feel supported and valued by faculty, peers, and mentors, they are more likely to be motivated to actively participate in academic and extracurricular activities, collaborate with others, and contribute to the overall success of the learning environment.
Building Confidence and Self-Efficacy
One of the most profound impacts of positive feedback is its ability to bolster students’ confidence and self-efficacy. When students receive recognition for their achievements and progress, they develop a stronger belief in their abilities and potential. This confidence not only empowers them to tackle academic challenges with greater assurance but also instills a sense of self-worth and resilience.
The Importance of Positive Feedback In Medical Education

Positive feedback plays a crucial role in helping medical students gain confidence in their abilities and skills. By receiving acknowledgment and recognition for their efforts and achievements, students develop a sense of validation and reassurance in their capabilities. When educators highlight specific strengths, improvements, and successes, students become more aware of their competencies and areas of expertise. It’s very easy to become discouraged and frustrated as a medical student, and this practice can go a long way in helping to build your students’ confidence.
Moreover, constructive feedback that focuses on affirming students’ progress while offering guidance for further growth instills a sense of competence and mastery. As students internalize this positive feedback, they approach challenges with greater self-assurance, resilience, and a willingness to learn and improve. Overall, positive feedback catalyzes building confidence in medical students, empowering them to navigate their educational journey with conviction and competence.
Cultivating a Supportive Learning Environment
In an educational ecosystem characterized by mutual respect and encouragement, positive feedback plays a central role in fostering a supportive learning environment. When students feel valued and appreciated for their contributions by their professors, they are more likely to actively engage with their peers and educators, fostering a culture of collaboration and intellectual curiosity. Furthermore, a positive type of reinforcement cultivates trust and open communication between students and educators, facilitating meaningful dialogue and constructive feedback exchanges that drive continuous improvement.
Promoting Reflective Practice
Beyond its immediate impact on academic performance, positive feedback encourages students to engage in reflective practice, prompting them to critically assess their strengths, areas for improvement, and learning strategies. By encouraging self-reflection and self-assessment, educators empower students to take ownership of their learning journey, equipping them with the essential skills for lifelong learning and professional development.
10 Examples of Positive Reinforcement Techniques Used in Higher Education


Positive feedback in medical school can take various forms, tailored to specific situations and individual needs. Here are some types of positive reinforcements commonly used in medical education:
- Specific Praise: One of the most effective ways of implementing positive feedback is by acknowledging specific actions or behaviors that demonstrate proficiency or growth. For example, “Your thorough patient history-taking skills were evident during today’s clinical rotation. I appreciate your attention to detail and communication with the patient.”
- Encouragement: Offering words of encouragement to reinforce effort and perseverance. For instance, “I’m impressed by your preparation for this surgical case. Keep up the great work, and remember that your hard work will pay off.”
- Recognition of Improvement: Noticing improvements over time and providing feedback to affirm progress. For example, “Your surgical technique has noticeably improved since the start of the rotation. Your dedication to refining your skills is evident, and I’m confident in your continued growth.”
- Highlighting Strengths: Identifying and celebrating strengths and talents. For instance, “Your ability to collaborate effectively with your peers in problem-based learning sessions is commendable. Your contributions greatly enhance the group’s learning experience.”
- Positive Reinforcement: Reinforcing a desired behavior to promote its recurrence. For example, “Your empathetic approach to patient care is exemplary. Patients appreciate your compassion and professionalism, which contributes to positive outcomes and patient satisfaction.”
- Role Modeling: Recognizing positive behaviors by faculty or peers and using them as examples to inspire others. For instance, “I observed how you patiently explained medical terminology to a confused patient, demonstrating excellent communication skills. Your approach sets a great example for your peers.”
- Constructive Affirmation: Providing feedback that validates students’ efforts while offering constructive suggestions for improvement. For example, “You demonstrated a solid understanding of the cardiovascular system during rounds today. Keep asking questions and seeking clarification to deepen your understanding even further.”
- Celebrating Achievements: Celebrating milestones, accomplishments, or successes, whether academic, clinical, or personal. For instance, “Congratulations on successfully completing your first skin-to-skin surgical procedure. Your confidence and hand skills were evident, and it’s gratifying to see your growth as a future surgeon. Great job.”
- Peer Recognition: Encouraging peer-to-peer feedback and recognition to foster a supportive learning environment. For example, “During today’s simulation exercise, your teamwork and leadership skills were instrumental in effectively managing the patient’s condition. Your peers recognize and appreciate your contributions.”
- Personalized Feedback: Providing feedback tailored to individual learning styles, preferences, and developmental needs. For instance, “I noticed you prefer visual learning tools. Incorporating more diagrams and charts into your study routine can further enhance your understanding of complex concepts.”
The Positive Effects of Feedback
Positive reinforcement can be a powerful tool in stimulating new behaviors by providing physical rewards or incentives for desired actions. When individuals receive positive reinforcement for engaging in specific behaviors, such as completing tasks or demonstrating skills, they are more likely to repeat those behaviors in the future. This reinforcement system strengthens the pathways associated with the desirable behavior, making it more ingrained and habitual over time. By associating positive outcomes with certain actions, individuals are motivated to continue exhibiting those good choices, leading to the development of new habits and skills.
The Downside of Focusing on Negative Feedback in Higher Education
Focusing on negative consequences in higher education can be detrimental to a student’s growth in several ways. When students receive predominantly negative feedback, it can undermine their confidence and self-esteem, leading to feelings of inadequacy and discouragement in learning new skills. Constant criticism without recognition of effort or acknowledgment of progress can create a fixed mindset, where students believe their abilities are inadequate and unchangeable, rather than something that can be developed through effort and perseverance. This can result in a fear of failure and a reluctance to take risks or engage in challenging tasks.
Focusing on Negative Feedback Can Stunt Educational Growth
Moreover, an overemphasis on shortcomings and deficiencies can overshadow students’ strengths and potential, hindering their motivation and enthusiasm for learning. Instead of fostering growth and development, a focus on negative feedback can stifle creativity, innovation, and resilience, ultimately impeding students’ ability to reach their full academic and professional potential. Therefore, educators need to provide a balanced approach to feedback, emphasizing constructive criticism while also recognizing and celebrating students’ efforts, progress, and achievements.
On a positive note, an encouraging classroom environment helps foster engagement and positive behavior among students. When students feel valued, respected, and supported, they are more likely to actively participate in learning activities and interact positively with their peers and teachers. A welcoming atmosphere encourages students to express their thoughts and opinions without fear of judgment, leading to increased confidence and a sense of belonging. Additionally, educators who create a supportive and inclusive environment establish clear expectations and provide consistent feedback, which helps students understand boundaries and promotes accountability. By nurturing a culture of collaboration, empathy, and mutual respect, a positive classroom environment empowers students to take ownership of their learning journey and encourages better results and enhanced student participation.
Students Will Often Model Their Professor’s Behavior
The specific behavior of professors in medical training can profoundly influence learners in several ways. Firstly, professors serve as role models for aspiring healthcare professionals, and their demeanor, attitudes, and communication styles can shape students’ understanding of professionalism and ethical conduct. Positive role modeling can inspire learners to emulate desirable traits such as empathy, integrity, and dedication to patient care. Conversely, bad behavior or attitudes may undermine students’ confidence and commitment to the profession.
Furthermore, the teaching approach of professors can significantly impact learners’ engagement and comprehension. Professors who demonstrate enthusiasm, clarity, and approachability can create an environment conducive to active learning, where students feel motivated to participate and ask questions. Conversely, educators who are disorganized, unresponsive, or dismissive may negatively affect students’ behavior and prevent them from seeking clarification or actively engaging in their studies.
Additionally, the feedback and support provided by professors play a crucial role in learners’ development. Constructive feedback delivered respectfully helps the entire class recognize their strengths and areas for improvement, fostering a growth mindset and facilitating skill enhancement. Conversely, harsh criticism or lack of feedback can demotivate learners and hinder their progress.
Overall, the behavior of professors in medical training profoundly influences learners’ professional development, attitudes toward patient care, and academic success. Positive role modeling, effective teaching strategies, and supportive mentorship play an important role in creating a conducive learning environment that nurtures the growth and success of future healthcare professionals. In my experience, this is the best way to keep students engaged and excited about learning.
Positive Reinforcement in Education – Conclusion
At the end of the day, the impact of positive reinforcement in higher education cannot be overstated. From fostering a growth mindset and enhancing motivation to building confidence and cultivating a supportive learning environment, positive feedback is an effective tool that enhances student success and holistic development. There are many different ways to implement positive reinforcement in the classroom and clinical settings as stated above. By recognizing and celebrating students’ achievements, educators not only inspire academic excellence but also nurture the next generation of lifelong learners and leaders.
Remember, feedback is not just about pointing out mistakes; it’s about celebrating progress and fostering growth.