Authored by Dr. Leland Jaffe, Associate Dean and Professor; Published on August 29th, 2024
Understanding what shapes our health often goes beyond genetics and medical care. Social determinants of health (SDOH)—like where we live, work, and play—play a huge role. They impact everything from our risk of chronic diseases to our lifespan.
Why does this matter? Because addressing these social factors can lead to better health outcomes for individuals and communities. In this post, we’ll explore what SDOH are and why they’re crucial for improving public health. Whether it’s income, education, or neighborhood safety, each factor has a ripple effect on our well-being.
Get ready to see how unlocking these determinants can pave the way for healthier lives.
Understanding Social Determinants of Health

To truly understand how health is shaped, we must look beyond doctors and hospitals. Social determinants of health (SDOH) are key elements that include our living conditions, education, and even our social interactions. These factors heavily influence our well-being.
Definition and Scope
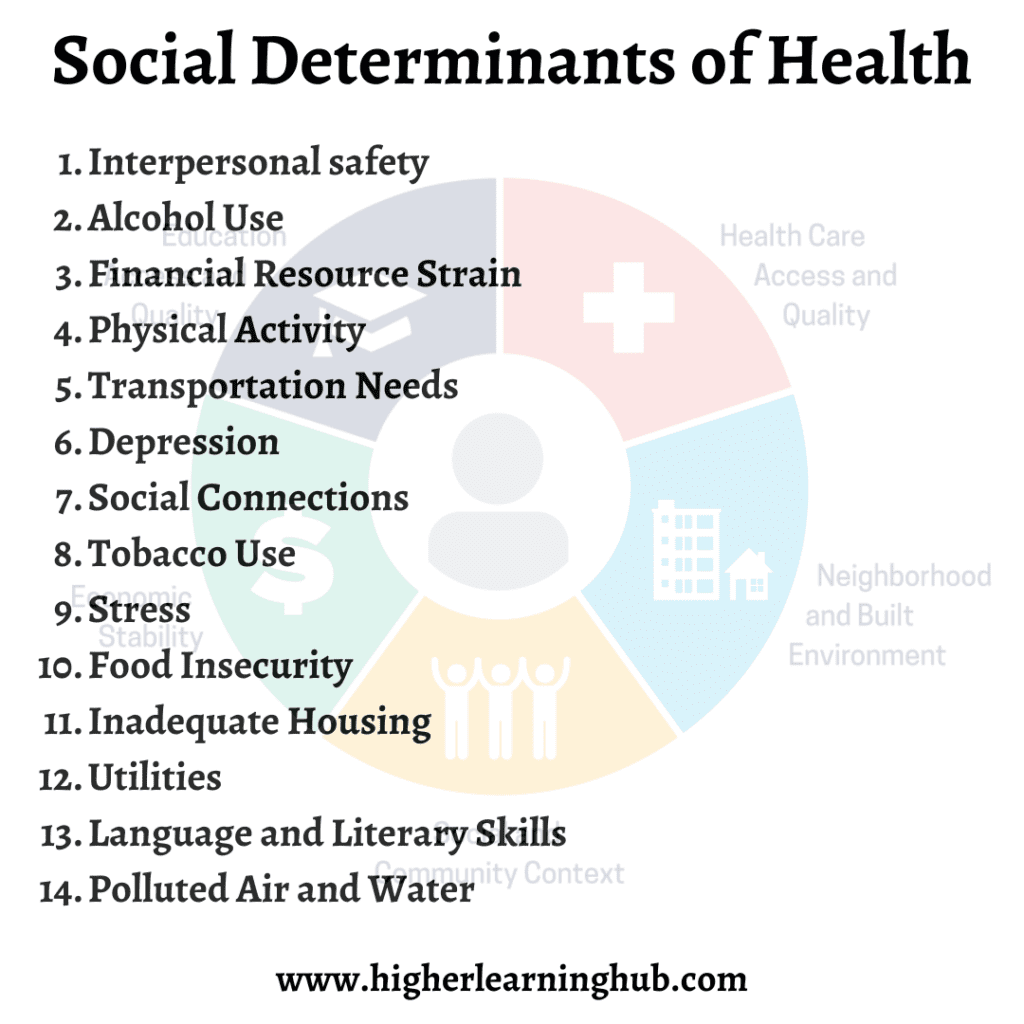
Social determinants of health are conditions in the places where people live, learn, work, and play. They affect a wide range of health risks and outcomes. Here are the main factors that come under SDOH:
- Socioeconomic Status: Includes income, wealth, and social class. People with higher socioeconomic status usually have better access to resources, which can lead to better health outcomes.
- Education: Higher education often leads to better job opportunities and more knowledge about healthy living.
- Neighborhood and Physical Environment: This includes the safety of the area, access to parks, and healthy food options. Living in a safe, clean area can reduce stress and promote physical activity.
- Employment: A stable job provides income, health insurance, and other benefits that contribute to health. Job security also reduces stress.
- Social Support Networks: Strong relationships with family, friends, and the community can provide emotional support and reduce stress.
- Access to Healthcare: Easy access to medical services ensures that people get the care they need when they need it.
By understanding these factors, we can see how various aspects of daily life affect our health.
Historical Context
The concept of social determinants of health has evolved over time. In the early 19th century, public health was mainly about sanitation and infectious diseases. During this period, there was little focus on how social factors affected health.
As time went on, researchers began to notice that people’s living conditions had a big impact on their health. They started to study these factors more closely. By the late 20th century, the term “social determinants of health” became more widely recognized.
Public health organizations began to include social factors in their health policies. They realized that improving living conditions could lead to better health outcomes for entire communities. Today, SDOH are an essential part of public health strategies worldwide.
This historical understanding shows us that improving health isn’t just the job of doctors. It’s about creating environments where everyone has the opportunity to live a healthy life.
Key Social Determinants of Health


Understanding the various social determinants that impact health is crucial. These factors can deeply influence our well-being. Below, we explore five main determinants and their specific effects on health outcomes.
Economic Stability
Economic stability is a foundation for good health. When people have steady jobs and reliable incomes, they can afford healthcare, nutritious food, and safe housing. These elements are vital for a healthy life.


- Income: Higher income allows for better access to medical care, healthier food options, and safer neighborhoods. Conversely, low income can limit these essential resources, leading to poorer health.
- Employment: Secure employment provides health insurance and other benefits, reducing financial stress. Job loss or unstable work can cause anxiety, leading to mental and physical health issues.
- Financial Stability: Financially secure individuals can manage unexpected medical costs and invest in their health. Poor financial stability can result in skipped medical appointments and neglected health needs.
Education Access and Quality
Education is a powerful tool for improving health. It equips individuals with the knowledge and skills needed to lead healthy lives.
- Literacy Rates: Higher literacy rates enable people to understand health information, follow medical advice, and make informed health decisions.
- Quality of Education: Access to quality education often leads to better job opportunities and higher income. This can directly affect access to health resources and services.
- Lifelong Learning: Continuous learning opportunities encourage people to stay informed about health advancements and adopt healthier lifestyles.
Healthcare Access and Quality
The availability and quality of healthcare services are pivotal in determining health outcomes. Easier access to high-quality care leads to better health.
- Access to Services: When people can easily access healthcare services, they are more likely to receive preventive care, early diagnosis, and timely treatment.
- Quality of Care: High-quality care ensures effective treatment and management of health conditions. Poor quality care can lead to misdiagnoses and inadequate treatment, worsening health conditions.
Neighborhood and Built Environment
The places where we live have a profound impact on our health. Safe, well-maintained neighborhoods can enhance well-being, while neglected areas can pose health risks.
- Housing Quality: Good housing protects against hazards like mold, lead, and overcrowding, which can cause chronic health issues.
- Transportation: Reliable public transportation and safe walking paths facilitate access to jobs, schools, and healthcare, promoting physical activity and reducing stress.
- Access to Nutritious Foods: Proximity to grocery stores with fresh, healthy food options supports balanced diets. Food deserts can lead to poor nutrition and related diseases.
Social and Community Context
Our social and community environments play a key role in shaping our health. Strong social networks and supportive communities foster better health outcomes.
- Social Support Networks: Positive relationships with family, friends, and neighbors provide emotional support, reducing stress and promoting mental health.
- Community Engagement: Being active in the community can enhance a sense of belonging and purpose, contributing to overall well-being.
- Societal Norms: Cultural norms and societal attitudes can influence health behaviors, from dietary habits to seeking medical care.
Each of these social determinants interconnects to shape our health. By addressing these areas, we can improve health outcomes for individuals and entire communities.
Impact of Social Determinants on Health Disparities
Social determinants of health (SDOH) significantly impact health disparities, creating differences in health outcomes among various populations. Whether it’s race, income, or location, these factors influence the quality of life and longevity. Let’s dive into how these elements play a role in different groups.
Racial and Ethnic Disparities
SDOH impacts health outcomes in various racial and ethnic groups. Often, these groups face unique challenges due to historical and systemic inequalities.
- Access to Healthcare: Many minority communities have less access to healthcare services. The lack of clinics or hospitals in their neighborhoods means fewer people get the preventive care they need. This can lead to untreated chronic conditions.
- Living Conditions: Historically marginalized groups often live in areas with poor housing conditions. Issues like mold, pests, and overcrowding can exacerbate health problems like asthma and stress.
- Education and Employment: Educational opportunities are often limited in minority communities. This affects job prospects and income levels, which in turn impacts health. Fewer educational resources can also mean less knowledge about healthy lifestyles.
Socioeconomic Disparities
Economic disparities play a critical role in health and well-being. People with higher incomes and better jobs generally enjoy better health.
- Income Inequality: Wealthier individuals can afford top-notch healthcare, nutritious food, and safer living environments. On the other hand, lower-income families may have to choose between paying for medical bills or groceries.
- Job Security: Stable employment provides not just a paycheck but also health insurance and other benefits. Unemployment or unstable jobs can lead to stress, anxiety, and poor health outcomes.
- Financial Barriers: Out-of-pocket medical costs can deter low-income individuals from seeking timely medical care. This means minor health issues can turn into serious problems.
Geographic Disparities
Where you live can hugely affect your health. Urban and rural areas offer different sets of challenges and benefits.
- Urban Areas: Cities often have more healthcare facilities, but they can also be crowded and stressful. Pollution and high crime rates can also impact health. On the upside, urban residents usually have better access to public transportation and job opportunities.
- Rural Areas: Rural communities often face a lack of healthcare facilities and specialists. Long distances to hospitals and clinics can delay essential care. However, rural areas often have a closer-knit community that offers strong social support.
- Environmental Factors: Geographic location can determine exposure to environmental hazards. For example, people living near factories or highways may face higher pollution levels, impacting respiratory health.
Understanding these disparities helps us see the bigger picture. It’s not just about individual choices but also about the environments we live in and the resources we have access to. Addressing these social determinants is essential for improving health outcomes for everyone.
Strategies to Address Social Determinants of Health
While understanding social determinants of health (SDOH) is essential, taking action is even more critical. Effective strategies can significantly improve health outcomes. This section explores various methods—policy interventions, community-based approaches, and healthcare system changes—that can tackle these determinants head-on.
1. Policy Interventions
Government policies play a pivotal role in combating social determinants of health. These regulations can level the playing field and ensure everyone has access to essential resources.
Healthcare Reforms
Healthcare reforms can ensure more people have access to necessary services. Universal healthcare systems, for example, provide medical assistance to all citizens, reducing disparities caused by income and employment status.
- Medicaid and Medicare Expansion: These programs can cover more low-income and elderly individuals, ensuring they get the care they need.
- Affordable Care Act: Policies like this extend coverage to those who were previously uninsured, closing gaps in access to healthcare.
Economic Policies
Economic policies can directly impact health by reducing poverty and improving living conditions. When people have better financial stability, they can afford healthier lifestyles.
- Minimum Wage Laws: Raising the minimum wage can provide families with more resources to live healthier lives.
- Tax Credits: Policies like the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) provide financial relief to low-income families, reducing stress and improving mental health.
Housing Policies
Housing directly impacts health. Safe, affordable housing can make a big difference in one’s well-being.
- Affordable Housing Initiatives: Programs that ensure affordable rent and mortgages help families live in healthy environments.
- Zoning Laws: Implementing zoning laws that provide green spaces can enhance mental and physical health.
Government policies can create a framework that supports healthier living conditions for everyone. These regulations not only provide immediate benefits but also long-term improvements in public health.
2. Community-Based Approaches
Communities are the backbone of social health. Local projects and programs can have a profound impact on the determinants of health.
Successful Community-Driven Projects
Several community-driven initiatives have shown remarkable success in improving health outcomes by addressing SDOH.
- Urban Gardening Projects: These initiatives provide fresh produce in food deserts, improving nutrition and fostering community engagement.
- Safe Streets Programs: These programs enhance neighborhood safety by improving lighting, creating pedestrian zones, and organizing community watches.
- School-Based Health Centers: These centers provide healthcare services directly in schools, ensuring that children receive timely medical attention and health education.
Public-Private Partnerships
Collaborations between public agencies and private organizations can boost resources and expertise.
- Community Health Workers: Training locals to become health workers helps in spreading health awareness and providing support within the community.
- Local Business Engagement: Encouraging local businesses to support health initiatives can provide additional funding and resources.
Community Engagement
Community involvement ensures that interventions are tailored to the specific needs of the population.
- Town Hall Meetings: Regular meetings where residents can voice their concerns and suggest solutions promote transparency and trust.
- Volunteer Programs: Mobilizing volunteers for health and wellness activities can build a sense of community and ownership.
Community-based approaches tap into local knowledge and resources, creating sustainable and effective solutions for improving social determinants of health.
3. Healthcare System Changes
Healthcare systems need to evolve to better address social determinants of health. By integrating services and focusing on preventive care, healthcare systems can offer more comprehensive support to individuals and communities.
Integration of Social Services
Integrating social services with healthcare ensures a holistic approach to patient well-being.
- One-Stop Health Clinics: Clinics that offer medical care along with social services like housing assistance, food aid, and mental health support can address multiple SDOH in one visit.
- Case Management: Assigning case managers to patients with complex needs helps coordinate care and connect them to necessary resources.
Preventive Care Focus
Shifting the focus from treatment to prevention can reduce the long-term impact of SDOH.
- Health Screenings: Regular screenings for chronic diseases can catch issues early and prevent more severe health problems.
- Patient Education: Educating patients about healthy habits and preventive care measures can empower them to take control of their health.
Training Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare providers need training to understand and address SDOH effectively.
- Cultural Competence Training: Training in cultural competence helps healthcare professionals provide better care to diverse populations.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Encouraging collaboration between healthcare providers and social workers ensures a comprehensive approach to patient care.
By implementing these changes, healthcare systems can more effectively address the social factors that impact health, leading to better outcomes for all.
Addressing social determinants of health requires a multi-faceted approach. Policy interventions, community-based projects, and healthcare system changes can collectively create a healthier environment for everyone. By taking these actions, we can move closer to a world where every individual has the opportunity to live a healthy, fulfilling life.
Social Determinants of Health – Conclusion
Addressing social determinants of health is crucial for improving overall well-being. By focusing on factors like economic stability, education, and neighborhood safety, we can make meaningful strides in public health.
These targeted interventions don’t just help individuals; they uplift entire communities. When we understand and act on these determinants, we pave the way for healthier, longer lives.
Every effort counts, and the time to act is now. By implementing effective strategies, we can create environments where everyone has the opportunity to thrive.